Cabbage Juice Benefits Ulcer Therapy
Fermented cabbage juice has long been used as an ulcer therapy., which explains why the active ingredient, s-methylmethionine itself is referred to as Vitamin U. Vitamin U," is a naturally occurring compound found in various plant sources, including cabbage and other vegetables. Vitamin U benefits ulcers, and improves leaky gut as it reduces inflammation and associated symptoms of GERD, reflux and and pain below the sternum and towards the mid area of the back.
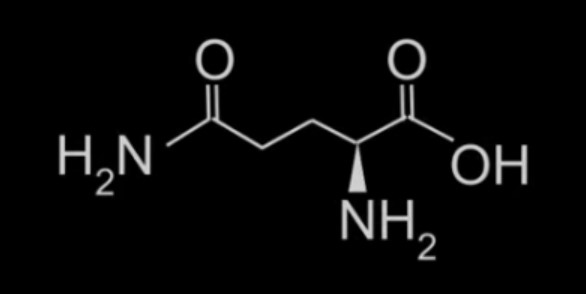
The molecular structure of s-methylmethionine (SMM) itself is derived from methionine, an essential amino acid. The chemical structure of SMM includes a sulfur atom (S) and a methyl group (CH3). SMM is produced in plants through the methionine salvage pathway, which involves the conversion of methionine to SMM.
In addition to its potential benefits on the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, the consumption of cabbage juice, which contains glutamine among its amino acid components, further supports GI health by providing essential nutrients that contribute to mucosal protection, anti-inflammatory effects, and overall GI well-being.
The Unique Benefits of S-methylmethionine (SMM) in Promoting Gastrointestinal Health
Gastrointestinal (GI) health is an important factor in managing methylation and improving liver detoxification. Disruptions in GI function often inlcude peptic ulcers and chronic gastritis. Poor condition of the peptic intestinal ultimately stresses not only the intestine, but also the bodys utilization of food, absorption of nutrients and puts stress on the liver due to immune complexes and large food molecule inflammatory reaction that results from a chronically inflamed intestinal wall.
While both SAMe, methionine and SMM contain methyl compounds, the effectiveness of S-methylmethionine (SMM) compared to methionine in addressing specific peptic ulcers or gastrointestinal health, is unique.
The benefits of SMM S-methymethionine as compared to simple methylation, with treating intestinal inflammation may be attributed to the SMM specific mechanisms of action and bioavailability:
- Mucosal Protection: SMM is believed to support mucin production, a glycoprotein that forms a protective barrier on the GI mucosal surface. This barrier shields the mucosa from gastric acid and irritants, contributing to mucosal protection. The bioavailability and specific attributes of SMM may make it well-suited to target this crucial aspect of GI health.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is often a contributing factor in GI conditions. SMM is identified as a peptic ulcer therapy as it modulates the production or activity of pro-inflammatory mediators, potentially reducing inflammation in the GI tract. Its direct influence on GI-specific inflammatory pathways distinguishes it from broader methylation processes.
- Tissue Repair and Regeneration: SMM may indirectly support tissue repair and regeneration in the stomach and duodenum, areas frequently affected by conditions like peptic ulcers. Methylation processes facilitated by SMM could contribute to DNA repair, protein synthesis, and cell proliferation, promoting tissue healing.
- Immune System Modulation: SMM might influence immune responses within the GI system, acting as a natural ulcer therapy by affecting responses to factors like Helicobacter pylori. While SAMe plays a vital role in immune cell function, SMM's actions in the GI tract could have a more direct impact on GI-specific immune mechanisms.
The Role of Methylation Status in GI Health
Individuals with low levels of methylation or SAMe might be more prone to gastrointestinal distress due to potential disruptions in various biochemical pathways involved in GI function. While methionine and SAMe supplements can contribute to overall methylation status, their effectiveness in addressing GI health and inflammation may differ from that of SMM.
Supplementing with vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine (SMM), may offer a specialized approach to support gastrointestinal health.
Vitamin U supplements with the greatest concentration of S-methylmethionine:
Recent Publication - Vitamin U Research
Effect of 6-month S-methylmethionine intake on the quality of life and dyspepsia symptoms in patients with chronic gastritis
[Article in Russian] V N Drozdov 1, E V Shih 1, A A Astapovskiy 1, L I Pavlova 1, I A Tormyshov 1, T M Ponomarenko 1Affiliations expand
PMID: 37346023 DOI: 10.33029/0042-8833-2023-92-2-80-86
Summarized:
Vitamin U, also known as S-methylmethionine (methylmethionine sulfonium chloride), has demonstrated its safety and s-methylmethionine benefits in various diseases, particularly in gastrointestinal conditions. In a recent study, researchers aimed to assess the impact of vitamin U intake on the symptoms of dyspepsia and the overall quality of life of individuals suffering from chronic gastritis.
The study involved 37 patients (21 men and 16 women) aged 35-60 years, all diagnosed with chronic gastritis of different etiologies. These patients were prescribed a daily dose of 300 mg of S-methylmethionine. To evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment, the researchers used the GSRS questionnaire (Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale) to assess dyspeptic symptoms and the SF 36 questionnaire to measure the quality of life. Assessments were conducted before the initiation of therapy, as well as after 3 and 6 months of receiving the dietary supplement.
The results of the study showed significant improvements in the patients' conditions over the course of therapy. Dyspeptic symptoms, which initially ranged from 3 to 9 points, saw a notable reduction, with a statistically significant decrease to 9 points by the 3rd month and an average score of 5.5 points by the 6th month. Additionally, according to the SF 36 questionnaire, various aspects of the patients' quality of life improved. This included physical functioning, bodily pain, social functioning, role-physical functioning, general perception of health, viability, role-emotional, and mental health.
This study highlights the positive impact of dietary supplements containing methylmethionine sulfonium chloride (vitamin U) at a dose of 300 mg per day in reducing the severity of dyspeptic symptoms in patients with chronic gastritis.
The findings indicate that vitamin U benefits in stabilizing the intestines. And because of this it can be argued that it is effective in improving the protective mucous membrane of the intestings and thereby correcting leaking gut, a condition that leads to absorption of incompletely digested foods causing allergies, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Potentially, by eliminating the need for proton pump inhibitors and other medications to treat peptic ulcer disease individuals are likely to digest and absorb foods better and minimize the impairment on the liver which takes place as a result of poor intestinal health and the effort required to metabolize the unpleasant prescription medications. .


